What is Quantum Computing? Imagine a computer so powerful it could solve problems in seconds that would take today’s supercomputers thousands of years. A machine that doesn’t just compute with ones and zeros but taps into the strange, mind-bending laws of quantum physics to process information in entirely new ways. That’s the promise of quantum computing—a technology that sounds like science fiction but is very much becoming science fact.
In this article, we’ll demystify quantum computing, answer the burning question: Do quantum computers exist?, and explore what you can expect in terms of quantum computer price in 2025. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a student, or a professional looking to stay ahead of the curve, you’ll walk away with a clear understanding of this revolutionary technology and what it means for the future.
What Is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a type of computation that uses quantum bits, or qubits, instead of the classical bits that traditional computers rely on. But what does that really mean? Let’s break it down.
How Do Quantum Computers Work?
Classical computers process information using bits, which can be either a 0 or a 1. Every app, website, and digital file you use is built on long strings of these binary digits.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, use qubits. Thanks to the principles of quantum mechanics, qubits can exist in a state called superposition—meaning they can be both 0 and 1 at the same time. This allows quantum computers to explore many possibilities simultaneously, making them exceptionally powerful for certain types of problems.
Another key quantum phenomenon is entanglement, where qubits become interconnected in such a way that the state of one qubit instantly influences another, no matter how far apart they are. This “spooky action at a distance,” as Einstein called it, enables incredibly fast and correlated computations.

What Problems Can Quantum Computers Solve?
Quantum computers aren’t meant to replace your laptop or smartphone. Instead, they excel at tackling complex problems that are impractical or impossible for classical computers, such as:
- Drug discovery and material science: Simulating molecular interactions to develop new medicines or advanced materials.
- Cryptography: Breaking current encryption methods—and creating new, quantum-safe ones.
- Optimization: Solving logistical challenges, like optimizing global supply chains or financial portfolios.
- Artificial intelligence: Accelerating machine learning algorithms and pattern recognition.
READ MORE : What is Agentic AI? 6 Ways Agentic AI May Soon Change the Way We Work?
Do Quantum Computers Exist?
Yes, quantum computers exist, but they’re still in the early stages of development. Think of them like the first room-sized computers of the 1940s—functional, but not yet practical for everyday use.
Current State of Quantum Computing
Companies like IBM, Google, Rigetti, and IonQ have built working quantum computers. In 2019, Google claimed “quantum supremacy” when its Sycamore processor performed a calculation in 200 seconds that would have taken the world’s fastest supercomputer 10,000 years.
However, these devices are far from perfect. Today’s quantum computers are prone to errors and require extremely controlled environments—often supercooled to near absolute zero (-273°C) to maintain qubit stability.
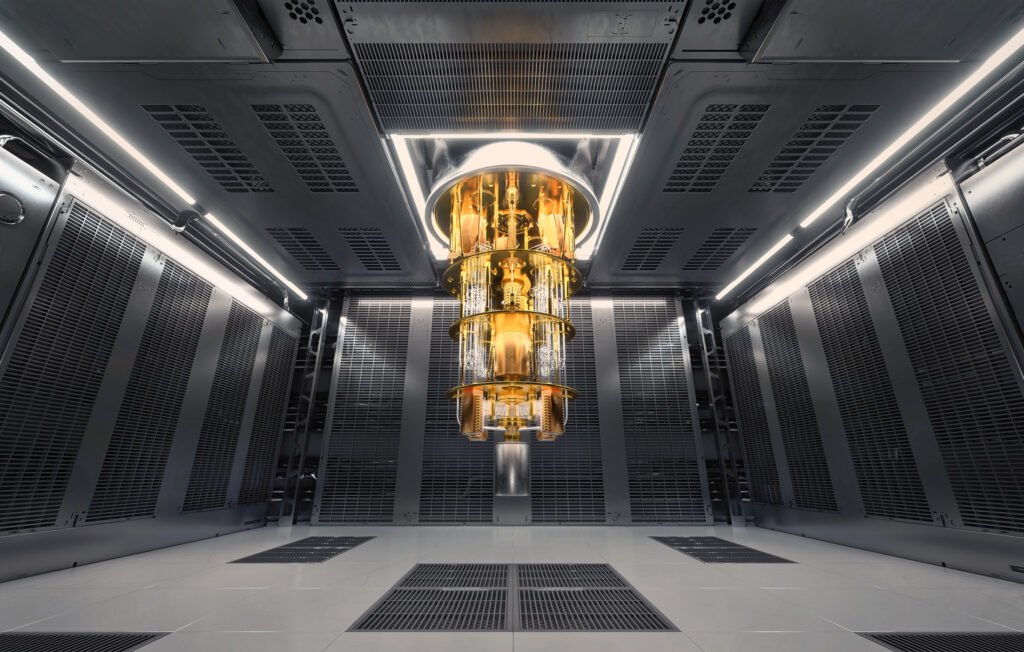
What Do Quantum Computers Look Like?
If you’ve ever wondered, What do quantum computers look like?, the answer might surprise you. They don’t resemble your desktop PC. In fact, most of what you see in photos is the cooling and shielding apparatus, not the processor itself.
A typical quantum computer setup includes:
- A dilution refrigerator to cool the qubits.
- Complex wiring and shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference.
- The quantum processor, which is often a small chip housed deep inside the system.
They look more like a piece of modern art or a high-tech chandelier than a computer!
READ MORE : 5 Game-Changing Tools Every Google AI Developers Should Know
How Much Does a Quantum Computer Cost in 2025?
Now for the big question: How much does a quantum computer cost? As of 2025, you still can’t buy a quantum computer for your home office. These machines are highly specialized, incredibly expensive, and primarily accessible via the cloud.
Breaking Down Quantum Computer Price
The cost of building and maintaining a quantum computer is astronomical. Here’s a rough breakdown:
- Research and development: Billions of dollars have been invested by companies and governments.
- Hardware costs: Cryogenic systems, precision components, and qubit chips alone can cost millions.
- Operating expenses: Keeping the system near absolute zero requires significant energy and maintenance.
For context, a commercial quantum computer from a company like IBM or D-Wave can cost anywhere from 10millionto10millionto15 million or more. And that’s just for the hardware—operating it adds millions more per year.
Cloud Access: The Affordable Alternative
Thankfully, you don’t need to buy a quantum computer to use one. Most providers offer cloud-based access, allowing researchers, developers, and businesses to run experiments remotely. For example:
- IBM Quantum offers free access to simulators and real quantum hardware through its cloud platform.
- Amazon Braket, Microsoft Azure Quantum, and Google Quantum AI provide similar services with pay-per-use pricing.
This model makes quantum computing accessible without the eye-watering quantum computer price tag.
What’s Next for Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is evolving rapidly. Here’s what to expect in the coming years:
Advances in Hardware
Researchers are working on making qubits more stable and scalable. New approaches, like topological qubits and error-corrected systems, could lead to more reliable and powerful quantum computers.
More Accessible Tools
As software and development platforms improve, more people will be able to experiment with quantum algorithms—even without a deep background in physics.
Industry Applications
From finance to pharmaceuticals, industries are already exploring quantum computing. In the near future, we may see quantum-assisted breakthroughs in climate modeling, renewable energy, and more.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is no longer a distant dream—it’s a reality, with working machines solving real-world problems today. While you won’t be buying a quantum computer for personal use anytime soon, cloud access is making this transformative technology available to innovators worldwide.
As we look to 2025 and beyond, the quantum computer price may remain high for full-scale systems, but the value of quantum-powered insights will only grow. Whether you’re a developer, a business leader, or simply curious about the future, now is the time to start learning about quantum computing.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore IBM’s Quantum Experience or take an online course to understand how you can leverage quantum technology. The quantum revolution is here—don’t get left behind.
Follow us on